A Random Influx of DNA from a Virus Helped Vertebrates Become So Stunningly Successful
Insertion of genetic materials from a virus into the genome of a vertebrate ancestor enabled the lightning-quick electrical impulses that give animals with backbones their smarts
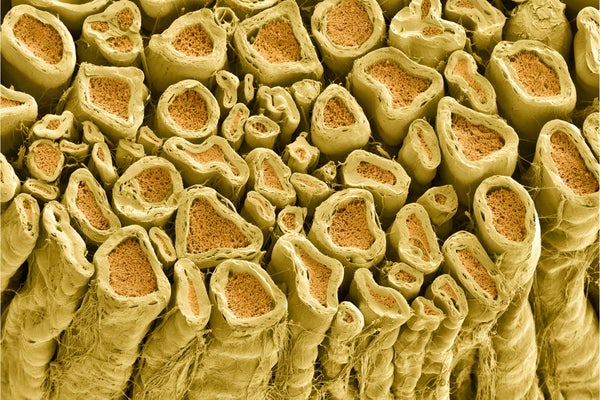
White myelin sheaths round rat nerve fibers.
NIH/Image Point FR/BSIP SA/Alamy Stock Photo
Charles Darwin proposed that evolution is pushed by gradual variations in organisms which have a survival benefit in a altering surroundings. But University of Maryland evolutionary biologist Karen Carleton says that scientists have lengthy grappled with the quandary that “evolution can occur abruptly, as described by Steven Jay Gould in [the theory of] punctuated equilibrium.” The query has all the time been: How does this occur?
A working example is the sudden look of myelin, the multilayered sheath on nerve fibers that remodeled the way in which neural impulses are carried out and turbocharged the transmission velocity of those impulses. Myelin seems out of the blue in vertebrates, animals with backbones that arose 500 million years in the past. Not a hint of it’s discovered within the ancestral line that preceded the arrival of vertebrates. A brand new examine within the journal Cell supplies a solution to this long-standing puzzle: the genetic directions to make myelin had been slipped into our vertebrate ancestor’s DNA by an infection with a virus.
Myelin is arguably probably the most important advance in nervous programs that ever occurred within the animal kingdom. The nice enhance in velocity of data transmission over lengthy distances within the physique is basically accountable for the dramatic leap in cognitive skill in vertebrates, to not point out velocity of motion and agility in canine, dolphins and other people, for instance, compared with invertebrates comparable to slugs, worms and starfish. Lacking myelin, neurons in invertebrates are clustered into teams (ganglia) located close to the physique buildings they management or that present sensory enter. There are ganglia subsequent to each swimming leg in a shrimp’s tail, for instance, however in vertebrates, neurons are massed collectively into one huge central meeting, the mind. The focus of billions of neurons right into a mind enabled cognitive capabilities nicely past these of invertebrates.
On supporting science journalism
If you are having fun with this text, think about supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you might be serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales concerning the discoveries and concepts shaping our world at this time.
Curiously, myelin is wrapped round nerve fibers by completely completely different cells within the physique (Schwann cells) than within the mind (oligodendrocytes). If myelin developed independently within the peripheral and central nervous system, transmission delays in both a part of the system would undermine the benefit, like a gradual Internet connection hobbling a high-speed laptop. But myelin seems absolutely fashioned concurrently within the mind and physique with the evolution of vertebrates. (One exception is the lamprey eel, probably the most primitive dwelling vertebrate, which has no myelin.) All of this raises the query: Where did myelin come from?
“Myelin evolution is a vital thriller and is completely understudied,” says myelin researcher Robert Gould on the Marine Biological Laboratory’s Whitman Research Center, who was not concerned within the new analysis. The examine reviews the involvement of what’s referred to as a retrovirus in precipitating the looks of myelination. Gould says that involvement of retroviral RNA in myelination is a shock—one that ought to have vital implications for myelin-related ailments, comparable to a number of sclerosis.
The central dogma in molecular biology holds that data flows from DNA within the cell nucleus and is carried outdoors the nucleus to the cytoplasm, the cell’s liquid inside, by one other molecule, messenger RNA. The messenger RNA transports a replica of the genetic code for a selected protein to ship to particular buildings within the cytoplasm that synthesize that protein. Viruses can not make proteins on their very own. Instead they hijack the molecular equipment of the cells they infect to make all of the viral proteins and enzymes wanted to generate new viruses.
Retroviruses such because the HIV virus perform this genetic hacking by reversing the sequence of the gene readout. They inject their RNA into the cells they infect, which serves because the code to make viral proteins. That RNA is transformed into DNA and, like malicious code in a software program program, will get inserted into the cell’s genome. When the cell reads out that rogue DNA code into RNA, it unwittingly makes the international viral proteins.
Dreadful infections and cancers are attributable to viruses corrupting our genome, however generally a viral an infection has sudden advantages, and mutant fragments of viral genes get completely mounted into the DNA of organisms and could be handed on for generations. These snippets of international DNA usually not make virus proteins. Still, they’ve a strong affect on what genes are learn out to make proteins by binding to DNA areas subsequent to genes and to proteins within the nucleus that management whether or not or not a gene is expressed. Astonishingly, 40 p.c of the DNA in mammals consists of remnants of those retroviral infections.
Myelin biologist Robin Franklin of the Wellcome Genome Campus in England and colleagues report within the new examine that they’ve recognized a retroviral ingredient in all vertebrates besides lampreys. The researchers have given this insertion into the genome of the widespread ancestor of vertebrates hundreds of thousands of years in the past the title RetroMyelin. They have proven that it stimulates the synthesis of proteins which might be important to creating myelin in each the central and peripheral nervous system.
When they blocked RetroMyelin in mouse cells in tradition—and in zebrafish larva and tadpoles—myelin largely didn’t kind. Further experiments revealed how blocking RetroMyelin stymied myelin manufacturing. A key protein in myelin referred to as MBP is crucial to kind the myelin sheath. The formation of myelin takes place as an extended, tentaclelike extension from a cell referred to as an oligodendrocyte envelops the nerve fiber.
To perform this course of, MBP on the internal floor of the oligodendrocyte’s cell membrane pairs up with the identical kind of molecule on the internal membrane of the oligodendrocyte’s elongated tentacle that wraps round a fiber. Binding to one another, MBP zips each inside surfaces of the membranes collectively like a folded piece of tape sticking to itself, and this squeezes out all of the cytoplasm to kind a compact sheath with excessive electrical resistance. The researchers confirmed that RetroMyelin latches onto a protein referred to as SOX10, a transcription issue that prompts the studying of DNA for the MBP gene. RetroMyelin stimulates SOX10, and in response the cells start producing massive quantities of MBP to make myelin.
“This is a really fascinating examine, which identifies an vital consider myelination,” says Klaus-Armin Nave, a myelin researcher on the Max Planck Institute for Multidisciplinary Sciences in Göttingen, Germany, who was not concerned within the analysis. “But considered rigorously, the conclusion that this retroviral an infection was the change that turned on myelination in vertebrates relies on correlation.” Myelination is a really advanced course of, he says, which should require many alternative proteins and mechanisms of gene regulation. The thriller of myelin could require additional sleuthing: there may be, as an example, little proof of MBP within the ancestors of vertebrates. “Where did MBP come from if there isn’t any DNA sequence for it in prevertebrates?” Robert Gould ponders. “Final proof,” Nave says, “could be to introduce the retroviral gene into lampreys and see in the event that they kind myelin.”
Retroviruses could be a highly effective engine of evolution, and myelin seems to be one of the exceptional examples. “It does make sense {that a} retrovirus may be concerned,” Carleton says. One hundred years after the invention of retroviruses and two centuries after a 22-year-old naturalist launched into his five-year crusing journey all over the world, molecular biology is now tackling the puzzle that Darwin grappled with in his momentous idea of evolution by illuminating how some traits seemingly seem out of nowhere.
