CHICAGO — Greater than electrical energy can illuminate a thundercloud.
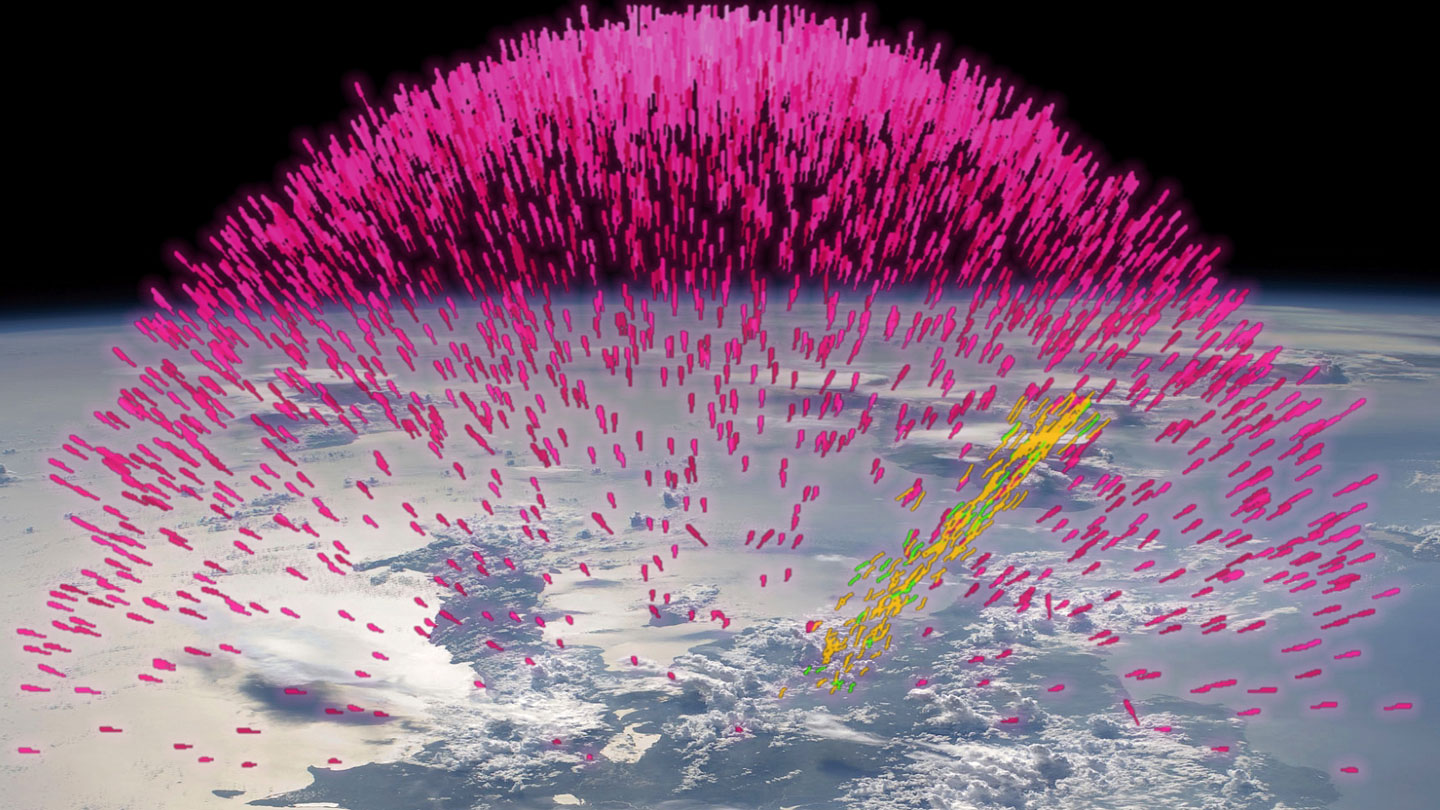
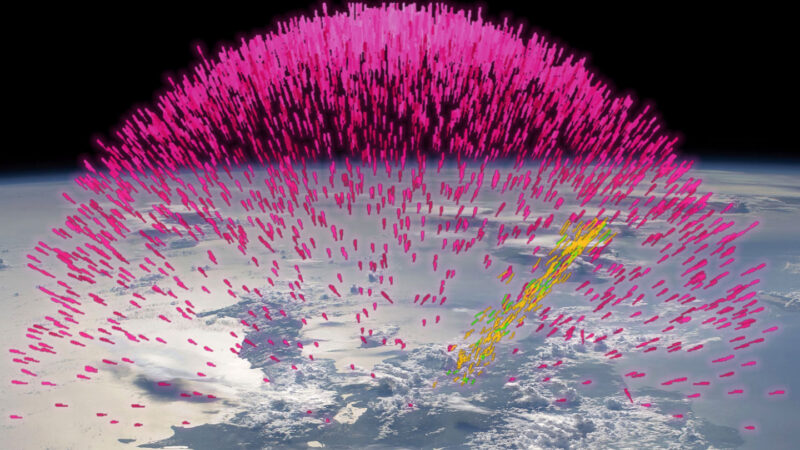
Good bursts of gamma radiation, often called darkish lightning or terrestrial gamma-ray flashes, additionally explode in lightning storms. And on uncommon events, these highly effective blasts — probably the most energetic radiation to naturally come up on Earth — may even strike a passing airplane, researchers reported December 13 on the American Geophysical Union assembly. The zap might briefly expose passengers to unsafe ranges of radiation.
First reported in 1994, darkish lightning is estimated to flash world wide a few thousand occasions every day. However scientists have solely a hazy understanding of the way it initiates. They typically agree darkish lightning is sparked by the electrical fields generated by thunderstorms and lightning bolts. These fields can spur electrons to velocities approaching the velocity of sunshine, amassing breakneck electron avalanches. When the streaming particles smash into airborne atoms, gamma radiation is unleashed.
Science Information headlines, in your inbox
Headlines and summaries of the most recent Science Information articles, delivered to your e-mail inbox each Thursday.
Thanks for signing up!
There was an issue signing you up.
Darkish lightning typically happens round 10 to fifteen kilometers excessive within the sky, altitudes frequented by airways. The brand new evaluation combines darkish lightning observations and airline routes to recommend that darkish lightning may strike close to a airplane round as soon as each 1 to 4 years, atmospheric scientist Mélody Pallu mentioned on the assembly. Nonetheless, that’s most likely “an higher restrict of the actual likelihood,” and even 10 occasions the precise charge, she mentioned, largely as a result of the calculations didn’t think about pilots’ avoidance of thunderstorms.
Earlier laptop simulations have revealed that passengers flying inside 200 meters of a powerful terrestrial gamma-ray flash’s initiation level might turn into uncovered to radiation doses exceeding 0.3 sieverts, mentioned Pallu, now on the Astroparticle and Cosmology Laboratory in Paris. Such ranges would surpass the occupational security degree of 0.02 sieverts per 12 months put forth by the Worldwide Fee on Radiological Safety.
Although considerably nebulous, the findings make one factor clear: Additional investigations are wanted to determine how darkish lightning impacts passengers flying by way of the sky.