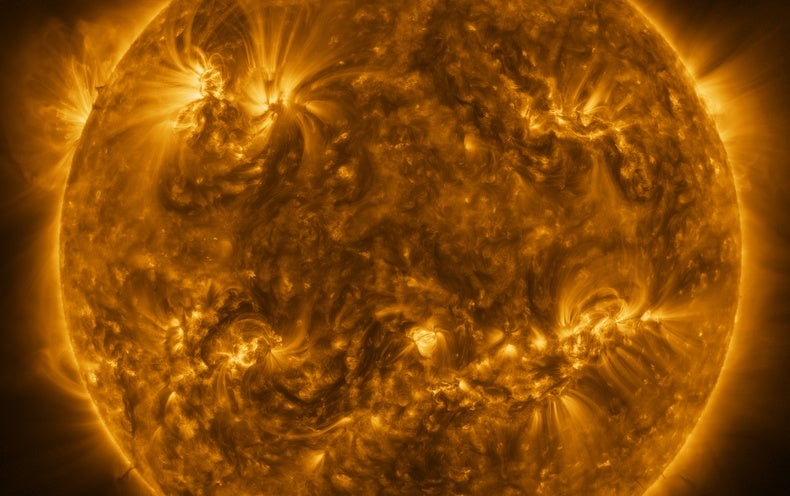
Is the solar an solely youngster? Or was it born right into a (very, very) large household?
The reply tells us extra than simply how awkward vacation household reunions may be (for those who assume yours are dangerous, think about how a lot worse it might be with a couple of thousand sibling rivals). After all, the solar’s origin story is, finally, our personal. We’ve seen big leaps in our understanding of how stars kind, however, satirically, we nonetheless have some fairly elementary questions left about our nearest, dearest one. Such as, whether or not the solar was born solo or together with an enormous passel of different stars.
Despite the solar being shut sufficient that we will nearly contact it, the largest drawback with discovering its origin story is that it’s previous. Born 4.6 billion years in the past, our star is effectively into center age and has wandered removed from its ancestral dwelling—some anonymous, now-vanished “stellar nursery” of gasoline that way back dispersed or consolidated into stars.
We can’t discover that nursery, however we will nonetheless find out about it. We have some proof of it, maybe surprisingly, within the type of meteorites, a few of which nonetheless carry clues in regards to the gestational atmosphere round them in the course of the beginning of the photo voltaic system. For instance, isotopes of parts like potassium inside meteorites have informed us the place within the presolar nebula they shaped, and variations between meteorites can be utilized to assist decide the nebula’s circumstances effectively earlier than the emergence of any planets.
With information from meteorites in hand and aided by state-of-the-art pc simulations, a world group of astronomers investigated the probably natal atmosphere of the solar and not too long ago printed its outcomes within the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. Using a intelligent line of reasoning, their analysis suggests the solar not solely had many siblings however spawned in fairly a metropolitan neighborhood.
Stars are born in cosmic clouds referred to as nebulae, forming when their interiors collapse onto a central pilelike level that turns into the nascent star. Nebulae are available many sizes and styles, from small darkish globules to immense big molecular clouds. How a star varieties in any given nebula is rather more a narrative of nature than of nurture.
For instance, the close by nebula Barnard 68 is a darkish clot of chilly gasoline and mud—tiny grains of silicates (rocky materials) and complicated carbon molecules just like soot—comparatively near us in area, only some hundred light-years away. It’s one in all my favourite objects; an eerie, pitch-black ghostly mass that totally blocks all gentle from stars behind it, like an opaque gap within the sky.
It’s solely half a light-year throughout (nearly three trillion miles), with barely sufficient materials in it to make a single star barely heftier than the solar. It’s probably in the course of that course of now, and will transmogrify itself right into a star in as little as 200,000 years.
On the opposite finish of the dimensions, now we have the Orion B molecular cloud advanced, a really huge website of energetic star formation that’s over a thousand light-years away and lots of tons of of light-years throughout. It’s beefy sufficient to make a staggering variety of stars—at the least 100,000 just like the solar. The iconic Orion nebula, seen to the bare eye and the birthplace of tons of of stars, is just one small a part of this big stellar manufacturing unit.
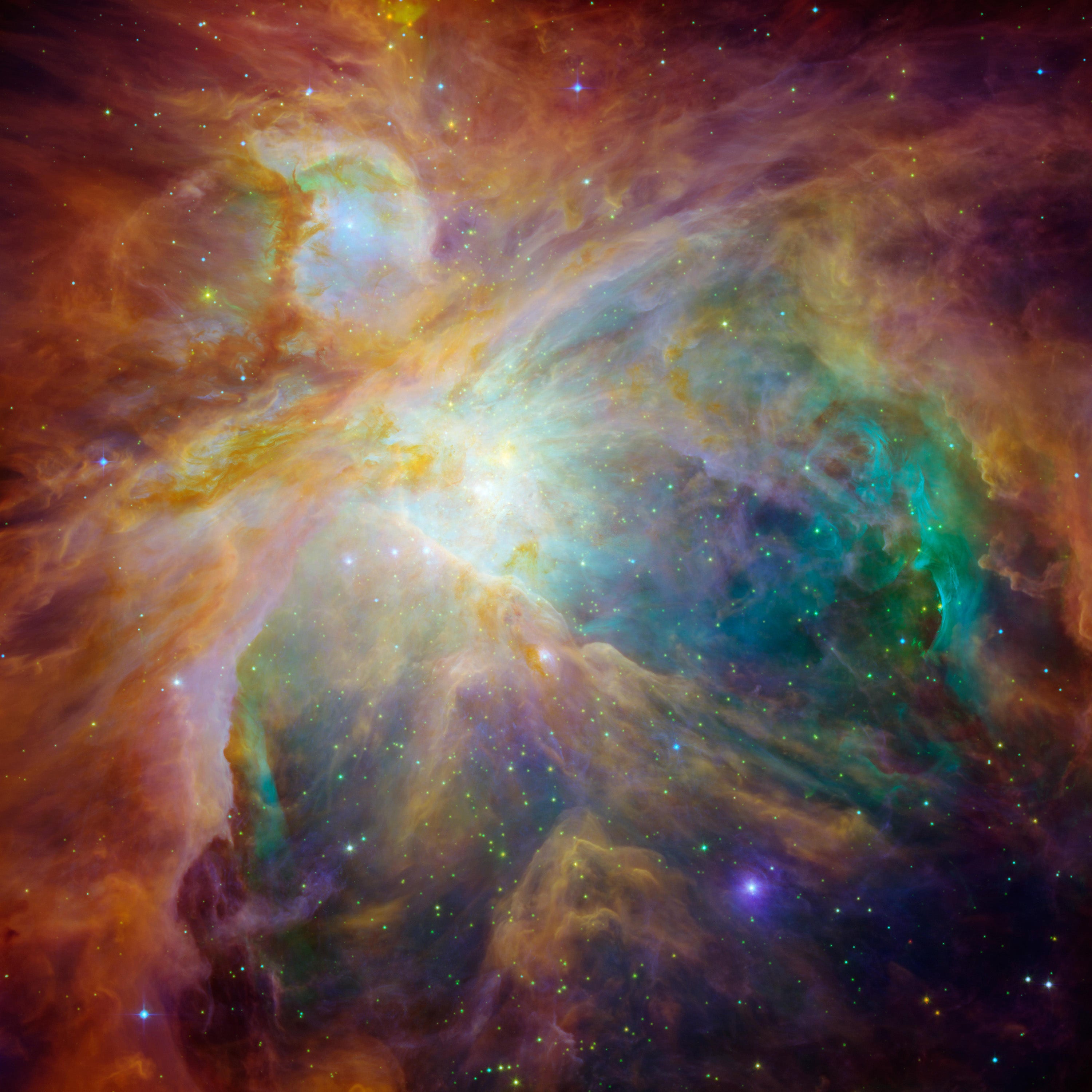

Giant clouds like this are comparatively uncommon however crank out stars on an industrial scale, whereas the smaller clouds are much less fecund however litter the galaxy. Just these numbers statistically it’s not attainable to discern the origin of the solar: it may have come from both form of stellar nursery.
However, these nebular environments are vastly totally different, which impacts the celebrities they create. Massive stars present in a nebula have an enormous affect on their gestating siblings. They can blast out fierce winds of subatomic particles—just like the photo voltaic wind however ramped up well beyond 11. These winds can seed forming stars with heavy parts like aluminum and magnesium. And later, after they explode as supernovae, they fling a unique combine of those parts, corresponding to iron and cobalt, a really great distance.
Massive stars, although, are uncommon. Maybe one out of 100 stars is huge sufficient to carry this form of sway, and small nebulae merely don’t make them. That means, in precept, wanting on the chemical composition of the early photo voltaic system may inform us in what sort of nursery the solar was born.
This was the main target of the newly printed analysis. The astronomers checked out two parts particularly: aluminum-26 and iron-60. Aluminum-26 is created inside large stars and blown out of their winds, whereas iron-60 is solid within the thermonuclear hell of an exploding star. Both parts are radioactive, decaying into magnesium and cobalt, so rigorously measuring the quantities of those daughter parts in pristine samples from the earliest days of the photo voltaic system—from meteorites, that’s—can inform us in regards to the atmosphere during which the solar shaped.
For their new evaluation, the worldwide group of scientists used the physics of nebulae and star formation to simulate a sunlike star’s beginning in quite a lot of environments, from nebulae containing only a few stars (a proxy for smaller clouds) as much as big ones with many hundreds. Next, they calculated the basic composition of the proto-proxy-presolar disk that emerged in every one, then in contrast these digital yields towards what’s truly measured in meteorites.
Their outcomes point out that because it shaped in its natal disk, the early solar was probably pummeled by highly effective winds and supernovae explosions—each sourced from large stars. That means the photo voltaic nursery was extra just like the Orion advanced than Barnard 68.
In different phrases, the solar was most likely extra of a downtown metropolis child than a rural small-town star. Of course, with its nebular nursery gone, we will’t verify this simply. After all, you may’t go dwelling once more.
And what of the solar’s siblings, the hundreds of different stars in its prolonged household? Like the solar, they as soon as nestled collectively like a litter of puppies, however probably wandered out on their very own eons in the past, and are actually orphaned, scattered throughout the galaxy. Still, astronomers do search for them—ones with the identical age and composition because the solar—in order that we will study extra about our mother or father star.
A reunion is fairly unlikely. If we wish to see a household album, we’ll simply must put it collectively ourselves.
This is an opinion and evaluation article, and the views expressed by the writer or authors usually are not essentially these of Scientific American.

