This article is a part of our unique IEEE Journal Watch collection in partnership with IEEE Xplore.
Trees play clear and essential roles in lots of ecosystems—whether or not they’re offering shade on a sunny day, serving as a house for a household of owls, or biking carbon dioxide out of the air. But forests are usually not solely diminishing by means of exploitative logging practices in addition to the method of desertification which turns grassland and shrubland arid.
Restoring biodiversity to those areas by means of rising new timber is an important first step, however planting seedlings in these arid environments could be each time and labor intensive. To tackle this downside, a crew of researchers at Firat University and Adiyaman University—situated in Elazig, Turkey and Adiyaman, Turkey, respectively—has developed an idea design of a robotic to drill holes and plant seedlings for as much as 24 hours at a time.
Andrea Botta is an engineering professor on the Polytechnic University of Turin in Italy who has researched the usage of agricultural robots. Botta, who didn’t contribute to this analysis, says that planting robots like this might fill an vital hole in communities with smaller labor forces.
“Robots are excellent at doing repetitive duties like planting a number of timber [and] also can work for an prolonged time frame,” Botta says. “In a group with a big lack of employees full automation is a good method.”
Tree-planting robots are usually not essentially a brand new idea and may tackle a wide range of sizes and shapes. In their work, the analysis crew in Turkey explored completely different current tree-planting robots, together with quadrupeds, ones with caterpillar belts, and wheeled robots. These robots, designed by teams comparable to college students at University of Victoria in Canada or engineers at Chinese tech large Huawei, both ran on steam, electrical batteries, or diesel. Several of the robots had been even designed to hold greater than 300 seedlings on their again at a time, reducing down on time spent going between a greenhouse and the planting website.
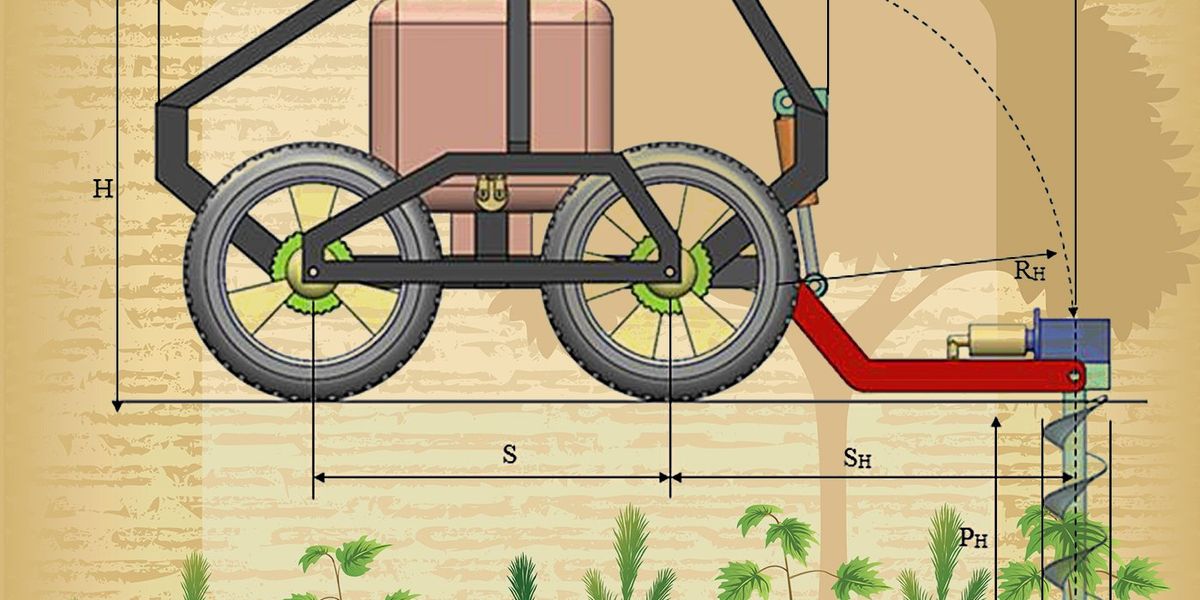
With these designs in thoughts, the analysis crew in Turkey developed a 3D mannequin of a robotic planter that had 4 wheels, a metal body, and a back-mounted hydraulic drill. Using diesel energy, this 136 kilogram robotic is designed to drive 300 centimeters at a time earlier than drilling a 50 cm gap for every seedling. In future iterations, the crew plans to include autonomous sensing.
“As a future research, we plan to fabricate the robotic we designed and develop autonomous movement algorithms,” the crew write of their paper (The researchers declined to remark for this story). “The fast growth of sensor know-how lately and the acceleration of analysis on the fusion of multi-sensor information have paved the best way for robots to achieve environmental notion and autonomous motion functionality.”
In explicit, the crew plan to mount environmental sensing models—together with cameras and ultrasonic sensors— to a gimbal on the robotic’s again. This sensor information will then feed into movement and object detection algorithms the crew plans to develop.
However, including extra autonomy to a lot of these robots doesn’t essentially imply they need to be given free rein over tree planting, Botta says. Especially in conditions the place they could be working alongside human employees.
“Human-robot collaboration is a really fashionable matter and ought to be fastidiously designed relying on the case,” he says. “Introducing automation to a job may additionally introduce issues too so it ought to be utilized appropriately contemplating the native communities and situation. For instance—if a big workforce is offered, the robotic ought to be designed contemplating a powerful synergy with the employees to ease their burden whereas avoiding harming the group.”
In future iterations of this design, Botta additionally hopes that consideration might be paid to variety within the planting surroundings and planting kind as effectively. For instance, including suspension to the robotic for higher all-terrain driving or including photo voltaic panels for supplemental energy and to permit the robotic to function the place different gas sources is probably not available. Adding a renewable energy choice to the robots might additionally assist be sure that they continue to be carbon-neutral whereas planting.
Considering how a robotic might deal with a number of varieties of vegetation would even be vital, Botta says.
“It appears that the majority—if not all—of the robotics options create tree farms, however in all probability what we want is planting precise forests with a big bio-diversity,” he says.
The work was offered in May on the 14th International Conference on Mechanical and Intelligent Manufacturing Technologies in Cape Town, South Africa.
From Your Site Articles
Related Articles Around the Web