Scientists have repurposed human abdomen cells into tissues that launch insulin in response to rising blood sugar ranges in a breakthrough that guarantees an efficient method to handle situations comparable to kind 1 diabetes.
The experiment, led by researchers from Weill Cornell Medicine within the US, revealed transplants of gastric insulin-secreting (GINS) cells reversed diabetes in mice.
Pancreatic beta cells usually do the job of releasing the hormone insulin in response to elevated sugar ranges within the blood. In folks with diabetes, these tissues are broken or die off, compromising their capability to maneuver glucose into cells for gas.
While GINS cells aren’t beta cells, they will mimic their operate. The intestine has loads of stem cells, which may rework into many different cell sorts, they usually proliferate rapidly. The hope is that these with diabetes might have their very own intestine stem cells remodeled into GINS cells, limiting the chance of rejection.
“The abdomen makes its personal hormone-secreting cells, and abdomen cells and pancreatic cells are adjoining within the embryonic stage of improvement, so in that sense it is not fully stunning that gastric stem cells could be so readily remodeled into beta-like insulin-secreting cells,” says Joe Zhou, an affiliate professor of regenerative medication at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York.
Scientists have been attempting to get one thing like this working for a few years, with none actual success. In this investigation, the workforce activated three particular proteins within the cells that management gene expression, in a specific order, to set off a transformaiton into GINS cells.
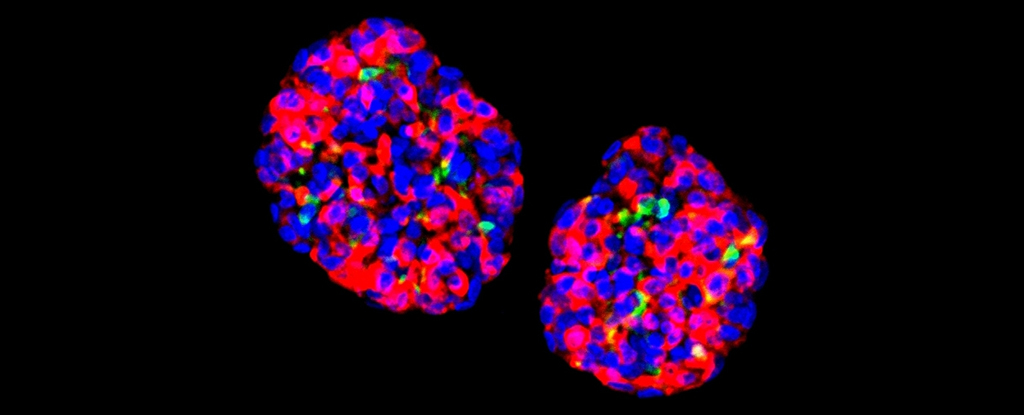
The reprogramming course of is extremely environment friendly, and when the cells have been grown in small clusters generally known as organoids they confirmed sensitivity to glucose. They have been then in a position to present long-lasting results on diabetes in mice.
Producing GINS cells from abdomen cells is not a very difficult course of, the researchers say. It solely wants a couple of days to occur, and these new organoids can final for a lot of months after being transplanted, based mostly on their checks.
“Gastric insulin-secreting (GINS) organoids exhibited glucose responsiveness 10 days after induction,” the researchers be aware of their report. “They have been steady upon transplantation for so long as we tracked them (6 months), secreted human insulin and reversed diabetes in mice.”
The insulin hormone is essential in regulating blood glucose. Without enough ranges we run the chance of a wide range of well being issues. Millions of individuals worldwide dwell with diabetes, principally utilizing insulin injections to assist maintain glucose ranges underneath management.
It’s nonetheless very early days for this method, however it will allow the physique to handle insulin ranges extra naturally once more. The researchers be aware a number of variations between human and mouse abdomen tissue that must be addressed in future research, whereas the GINS cells additionally must be made much less weak to immune system assault.
Initial indicators are promising although. The analysis provides to a lot of methods scientists need to sort out diabetes, together with weight loss plan enhancements and tweaking the best way that insulin is delivered to the physique.
“This is a proof-of-concept examine that offers us a strong basis for growing a therapy, based mostly on sufferers’ personal cells, for kind 1 diabetes and extreme kind 2 diabetes,” says Zhou.
The analysis has been printed in Nature Cell Biology.